What Are The Types Of Verbs In Urdu? | Verbs with Types

Verbs With Types in English and Urdu with Examples
In this blog, we will teach you types of verbs in English and Urdu with examples. Verbs play an important role while making sentences or talking about something, a sentence cannot give complete and clear meaning without a verb. Reading this blog will help you learn many types of verbs with their Urdu and English examples.
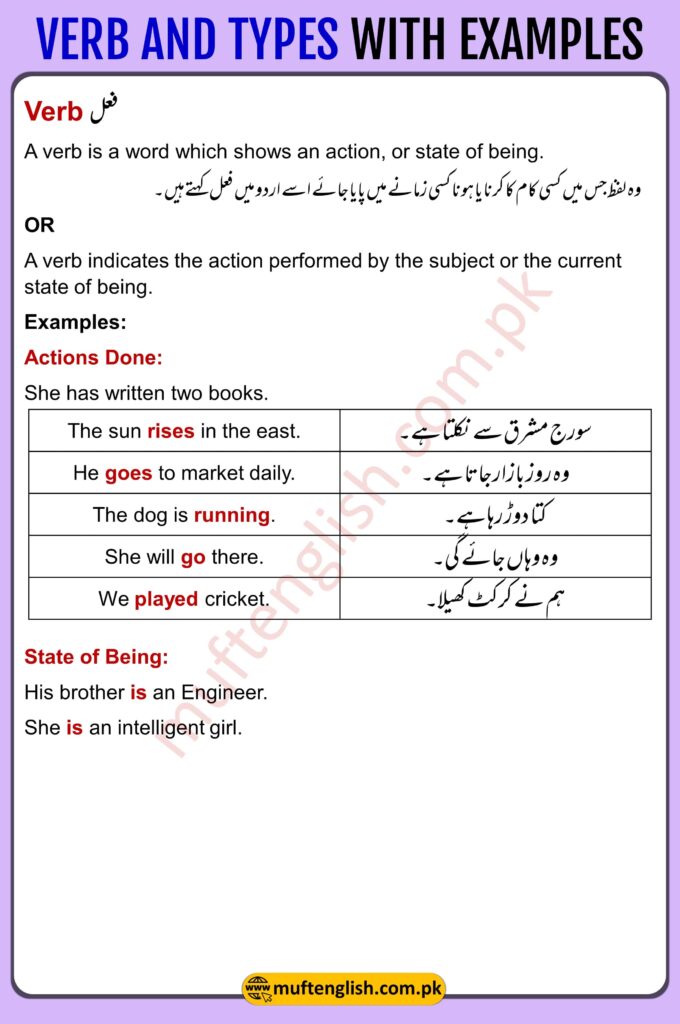
Verb – فعل
A verb is a word which shows an action, or state of being of the subject.
وہ لفظ جس میں کسی کام کا کرنا یا ہونا کسی زمانے میں پایا جائے اسے اردو میں فعل کہتےہیں۔
OR
A verb indicates the action performed by the subject or the current state of being.
Examples:
Action Done:
She has written two books.
| The sun rises in the east. | سورج مشرق سے نکلتا ہے۔ |
| He goes to the market daily. | وہ روز بازار جاتا ہے۔ |
| The dog is running. | کتا دوڑ رہا ہے۔ |
| She will go there. | وہ وہاں جائے گی۔ |
| We played cricket. | ہم نے کرکٹ کھیلا۔ |
State of Being:
His brother is an Engineer.
She is an intelligent girl.
Types of Verbs in English and Urdu with Examples
Verbs are divided into different classis.
فعل کو مختلف طبقات میں تقسیم کیا گیاہے۔
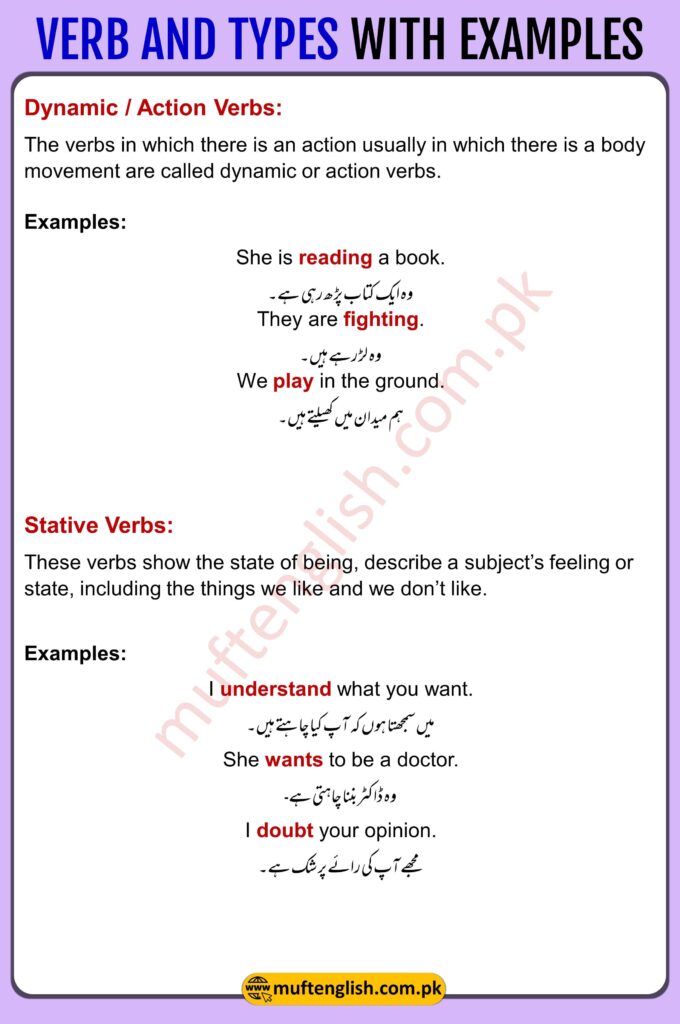
Dynamic / Action Verbs:
The verbs in which there is an action usually in which there is a body movement are called dynamic or action verbs.
Like: Play, Write, Go, Sit, Dance, Smile, etc.
وہ فعل جن میں جسم کی حرکت ہو۔
Examples:
She is reading a book.
وہ ایک کتاب پڑھ رہی ہے.
They are fighting.
وہ لڑ رہے ہیں۔
We play in the ground.
ہم میدان میں کھیلتے ہیں۔
He is cleaning his room.
وہ اپنے کمرے کی صفائی کر رہا ہے۔
Stative Verbs:
These verbs show the state of being and describe a subject’s feeling or state, including the things we like and don’t like.
ان الفاظ کا استعمال ہم تب کرتے ہیں جب ہم کسی کے حالت، احساسات، اور وہ چیزیں جوہم پسند اور نا پسند کرتے ہو۔
Like: Need, Want, Feel, Love, Hate, Understand, Believe, Like, Dislike, Prefer, Realize, Know, Doubt, agree, disagree etc.
Examples:
I understand what you want.
میں سمجھتا ہوں کہ آپ کیا چاہتے ہیں۔
She wants to be a doctor.
وہ ڈاکٹر بننا چاہتی ہے۔
I doubt your opinion.
مجھے آپ کی رائے پر شک ہے۔
Do you agree with me?
کیا تم مجھ سے متفق ہو؟
Remember we can’t use the stative verbs in continuous tenses. They are usually used in simple tenses, and occasionally in perfect ones.
Auxiliary Verbs:
There are three kinds of auxiliary verbs.
- Primary Auxiliary Verbs
- Modal Auxiliary Verbs
- Semi Modal Auxiliary verbs
Primary Auxiliary Verbs / Helping Verbs:
All the “be form” (is, am, are, was, were, been, have, has, had, Do, does) are called primary auxiliary or helping verbs.
Examples:
He is going to school.
وہ سکول جا رہا ہے۔
Were they playing?
کیا وہ کھیل رہے تھے؟
She has played well.
وہ اچھا کھیلی ہے۔
Modal Auxiliary Verbs:
Can, Should, Could, Ought to, May, Might, Would, etc. are called modal auxiliary verbs.
Examples:
She can play cricket.
وہ کرکٹ کھیل سکتی ہے۔
They could swim.
وہ تیر سکتے تھے۔
He may go there.
وہ وہاں جا سکتا ہے۔
Semi Modal Auxiliary Verbs:
Need and Dare are called semi-modal auxiliary verbs.
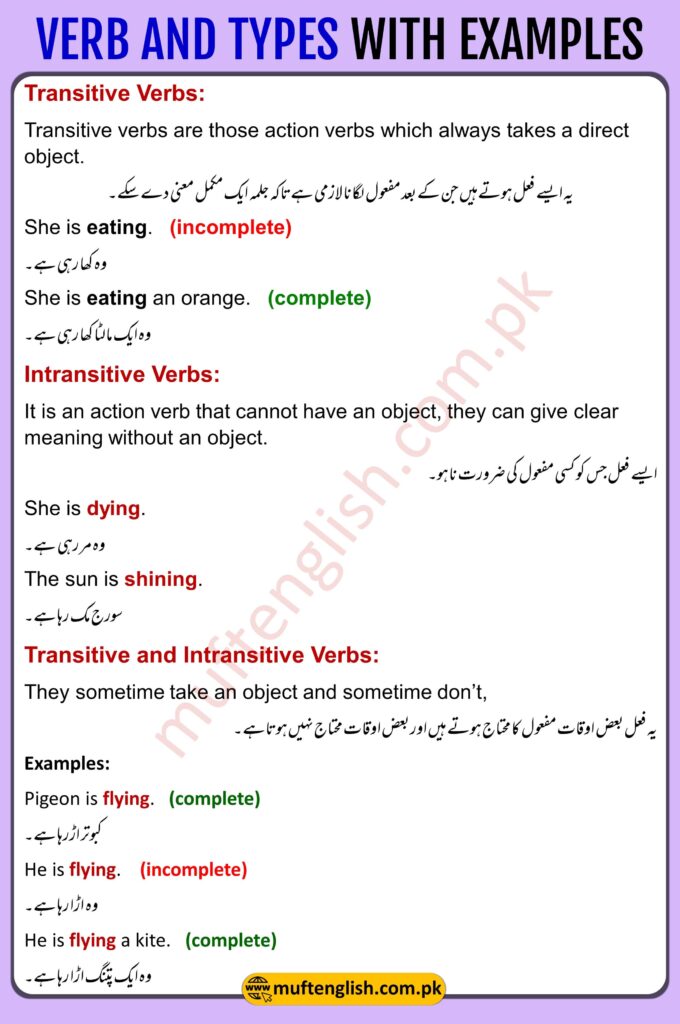
Transitive Verbs:
Transitive verbs are those action verbs which always takes a direct object.
یہ ایسے فعل ہوتےہیں جن کے بعد مفعول لگانا لازمی ہےتاکہ جلمہ ایک مکمل معنی دے سکے۔
She is eating. (incomplete)
وہ کھا رہی ہے۔
She is eating an orange. (complete)
وہ ایک مالٹا کھا رہی ہے۔
They are drinking. (incomplete)
وہ پی رہے ہیں۔
They are drinking milk. (complete)
وہ دودھ پی رہے ہیں۔
Intransitive Verbs:
It is an action verb that cannot have an object, it can give a clear meaning without an object.
ایسے فعل جس کو کسی مفعول کی ضرورت نا ہو۔
She is dying.
وہ مر رہی ہے۔
The sun is shining.
سورج چمک رہا ہے۔
He smiles.
وہ مسکرایا۔
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs:
They sometimes take an object and sometimes don’t, It sometimes gives complete meaning without an object and sometimes it is incomplete without an object and it does not give complete and clear meaning.
یہ فعل بعض اوقات مفعول کا محتاج ہوتے ہیں اور بعض اوقات محتاج نہیں ہوتاہے۔
Examples:
Pigeon is flying. (complete)
کبوتر اڑرہا ہے۔
He is flying. (incomplete)
وہ ـــــــــ اڑا رہا ہے۔
He is flying a kite. (complete)
وہ ایک پتنگ اڑا رہا ہے۔
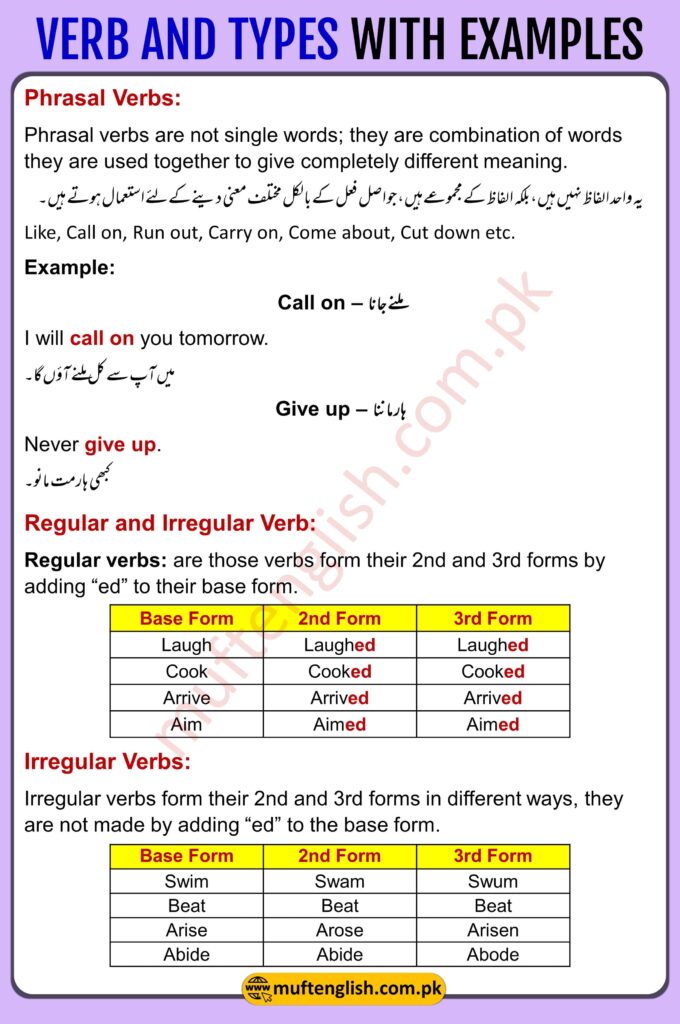
Phrasal Verbs:
Phrasal verbs are not single words; they are a combination of words that are used together to give completely different meanings.
یہ واحد الفاظ نہیں ہیں، بلکہ الفاظ کے مجموعےہیں، جو اصل فعل کے بالکل مختلف معنی دینےکےلئے استعمال ہوتے ہیں۔
Like: call on, Run out, Carry on, Come about, Cut down etc.
Example:
Call on – ملنے جانا
I will call on you tomorrow.
میں آپ سے کل ملنے آؤں گا۔
Give up – ہار ماننا
Never give up.
کبھی ہارمت مانو۔
Regular and Irregular Verb:
Regular verbs:
Those verbs that form their 2nd and 3rd forms by adding “ed” to their base form.
| Base Form | 2nd Form | 3rd Form |
| Laugh | Laughed | Laughed |
| Cook | Cooked | Cooked |
| Arrive | Arrived | Arrived |
| Aim | Aimed | Aimed |
| Walk | Walked | Walked |
| Peel | Peeled | Peeled |
| Visit | Visited | Visited |
| Arrange | Arranged | Arranged |
Irregular Verbs:
Irregular verbs form their 2nd and 3rd forms in different ways, they are not made by adding “ed” to the base form.
| Base Form | 2nd Form | 3rd Form |
| Swim | Swam | Swum |
| Beat | Beat | Beat |
| Arise | Arose | Arisen |
| Abide | Abide | Abode |
| Awake | Awoke | Awoken |
| Bite | Bit | Bitten |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk |
| Read | Read | Read |
Causative Verbs:
Read: Causative verb Make with Examples
Causative are used when we do not act directly, instead we get the action done by someone else (agent).
Verb and Types PDF
By learning these types of verbs and understanding their proper use with examples, you can improve your English speaking fluency and as well your writing skills. Get the PDF below and start learning.